Klinische Anwendungen
Viszeralchirurgie
Wichtigste klinische Anwendungsgebiete in der Viszeralchirurgie sind aktuell die intraoperative Beurteilung von Anastomosen, des Resektionsrandes im Rahmen kolorektaler Operationen sowie der Schlauchmagendurchblutung bei Ösophagusresektionen. Anhand von Wasser-, Hämoglobin- und Sauerstoffgehalt im Gewebe können intraoperativ Rückschlüsse auf dessen Vaskularisierung und Integrität geschlossen werden. Auch bei der Mesenterialischämie kann die HSI-Technologie sinnvoll zum Einsatz kommen, um das Resektionsausmaß grenzwertig perfundierten Darms festzulegen. Dabei ist die HSI-Technik ein objektives intraoperatives Entscheidungstool bei der Identifikation der optimalen Resektionslinie bzw. Anastomosenregion mit dem Ziel, das OP-Ergebnis zu optimieren, ideale Bedingungen für eine ungestörte Heilung zu schaffen und letztlich die Patientensicherheit zu erhöhen.
An verschiedenen Kliniken konnte die Machbarkeit der intraoperativen Beurteilung nahezu des gesamten Spektrums intestinaler Anastomosen in der Viszeralchirurgie (Ösophagus, Magen, Pankreas, Dünndarm, Kolon und Rektum) dargelegt werden.
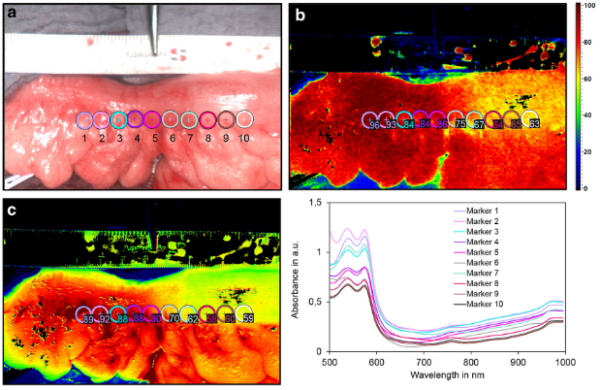
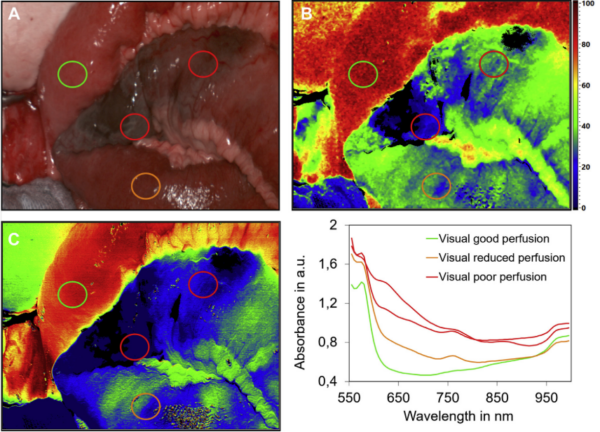
Zudem wird die HSI-Technologie zunehmend zur Gewebeklassifikation und Tumorerkennung im experimentellen Setting sowie auch bei chirurgischen Eingriffen in klinischen Forschungsarbeiten appliziert.