Klinische Anwendungen
Wundmedizin
Mit der TIVITA® 2.0 Wound Edition sind DiagnostikerInnen und KlinikerInnen in der Lage, Wunden jeglichen Ursprungs nicht-invasiv und innerhalb weniger Sekunden qualitativ und quantitativ zu beurteilen und Heilungsverläufe zu dokumentieren. So können (neuartige) Therapien und Therapieansätze objektiv bewertet und im zeitlichen Verlauf an patientenspezifischen Bedürfnisse angepasst werden.
Aktuell wird die HSI-Technologie in verschiedenen Kliniken und Wundzentren hauptsächlich zur Beurteilung chronischer Wunden vom Typ Dekubitus, Ulcus cruris venosum/arteriosum/mixtum oder Diabetischer Fußulcus verwendet. Diese entstehen meist als Symptom oder Komplikation einer bestehenden Grunderkrankung, wie der chronisch venösen Insuffizienz, der peripheren arteriellen Verschlusskrankheit oder des Diabetes mellitus.
In der Wundversorgung spielt die Gewebeoxygenierung für den Heilungsverlauf eine große Rolle. Ab einer Sauerstoffversorgung des Gewebes von ca. 50 % ist ein Heilungsverlauf sehr wahrscheinlich, während bei dauerhaften Oxygenierungswerten unter ca. 30 % das Gewebe aufgrund der Unterversorgung voraussichtlich absterben wird. Eine ermittelte Gewebesauerstoffsättigung von unter 10 % deutet auf nekrotisches Gewebe hin.
Gerade Wunden im Bereich der Beine und Füße führen bei den Patienten zu starken Schmerzen. Dieses wiederum hindert die Bewegung der Patienten, was für die Sauerstoffversorgung der Wunde und die Heilung nachteilig ist. Somit ist eine kontrollierte Dokumentation der Wundheilung eine wichtige Unterstützung bei der Wahl der Therapie.
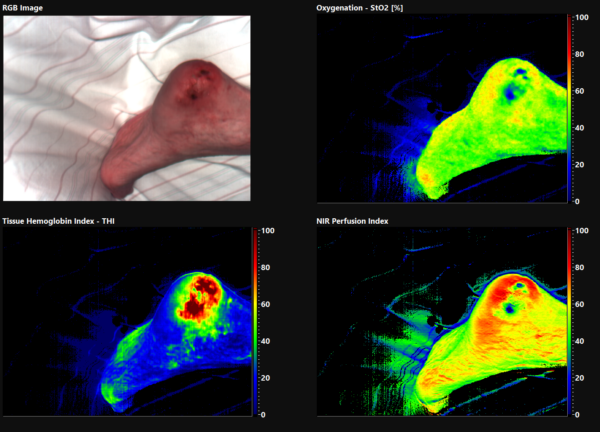
Mit hyperspektraler Bildgebung kann parallel zur Sauerstoffsättigung der Wassergehalt des Gewebes bestimmt werden. Daher können auch Ödeme gut beurteilt werden. Ödeme können andere Gefäße durch das Aufbringen von Druck in ihrer Funktionalität beeinträchtigen, was sich negativ auf die Sauerstoffversorgung des Gewebes auswirken kann. Eine andere Ansammlung von Flüssigkeit stellt ein Hämatom dar. Dabei tritt Blut aus verletzten Gefäßen aus und setzt sich im Körpergewebe bzw. einer Körperhöhle ab. Hämatome liegen meistens im subkutanen Bereich, wobei die Färbung durch die Gerinnung des Blutes bzw. Blutabbauprodukte entsteht. Im Unterschied zum Ödem lagert sich dabei kein Wasser ab. In solchen Bereichen ist der Hämoglobinwert eher erhöht und die Sauerstoffsättigung reduziert.